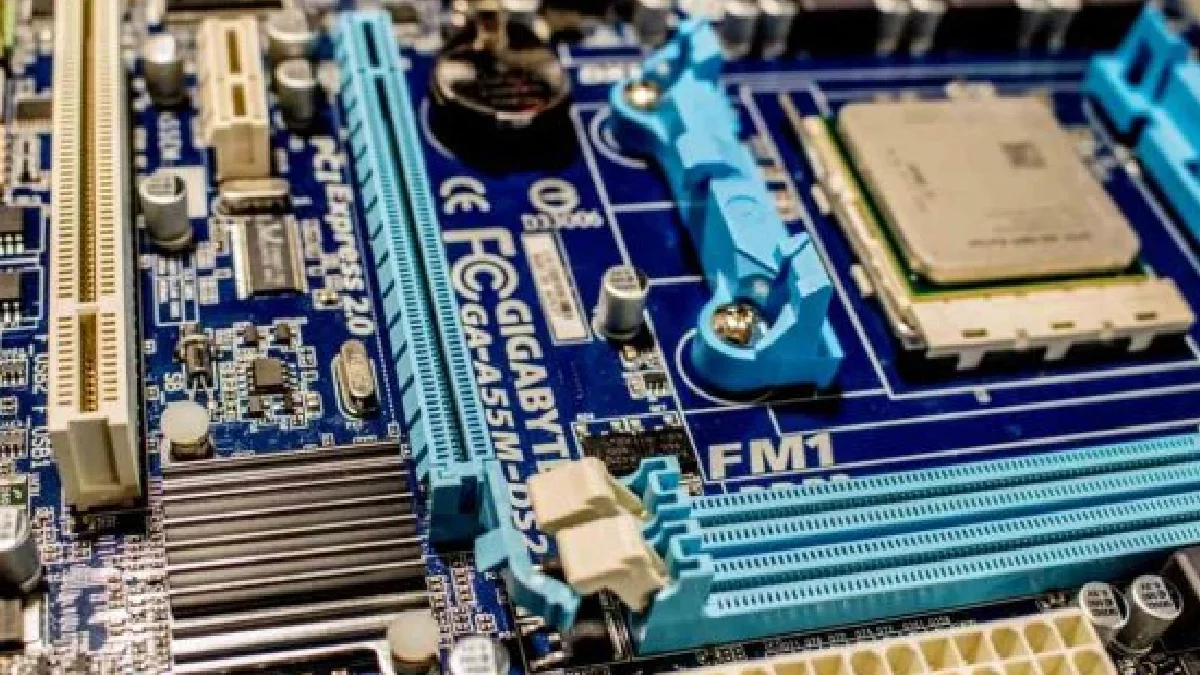
Best Motherboard for Intel Core i5-12600K – Motherboards only support the Alder Lake processor with Z690 chipset and LGA 1700 socket. You don’t need to spend wealth on a motherboard to mount the new Intel Core i5-12600K, as it doesn’t require a power-hungry design. However, you will have to stretch your inexpensive if you want to take advantage of DDR5 compatibility and improvements in the quality of its components.
Basically, in the coming months, more boards compatible with these processors will appear. Because they are state-of-the-art components that have just landed on the market in 2021, prices still have to be adjusted to be more competitive. We have selected the best options available at the moment for this processor, and we will update you with new releases.
Moreover, THANKS TO ITS IMPRESSIVE POWER CONFIGURATION AND COMPREHENSIVE SPEC LIST, the ASUS ROG Strix Z690-F Gaming is our go-to board for this processor.
However, the best value for money and therefore the one recommended as the best buy is the MSI PRO Z690-A WIFI
Get one of them and become one of the first to experience the superiority of the new 12600K.
Table of Contents
What to look for when choosing a motherboard for Intel Core i5-12600K Alder Lake
To mount Intel 12th GEN processors smoothly, you should look for an LGA 1700 socket.
Thermal solution:
We know that too much heat can affect overall system performance. That is why it is essential to consider the motherboard’s cooling. You can choose between optimized or comprehensive premium thermal solutions. Both are the same, to offer the cooling capacity to maintain the average temperature inside the plate.
Departures:
Please take a look at the port outlets it comes with. Must include Thunderbolt 4, USB 3.2 Gen 2 Type C and A, HDMI 2.1, and Display Ports 1.4 to connect more than one monitor. Connecting other devices with your board will no longer be a problem.
Memory:
In addition, having 128GB of the latest DDR5 memory will allow you to do anything. This temporary storage can hold more information for less time to process quickly.
Connectivity:
Having the best possible connectivity means PCIe 5.0 with 4x M.2 NVMe SSDs, Bluetooth 5.0, and Windows 11 compatibility. One of the greatest virtues a motherboard can offer is good connectivity.
Networking:
To play games faster or browse pages when you work, thanks to Wi-Fi 6 plus 2.5G LAN ethernet. You’ll have access to optimal wireless performance.
Types of sockets present on PC motherboards: Best Motherboard
Socket 1
Basically, old socket present on 486 boards. It had 169 pins and operated at 5 volts.
slot 2
Socket-1 update. It had 238 pins and was still running at 5 volts.
Socket 3
It contained 237 pins and operated at 5 volts but added the ability to work at 3.3 volts by setting the voltage via a jumper on the motherboard.
socket 4
Specially designed for use with early 5 volt 60 and 66 Mhz Pentium microprocessors. It had 273 pins and operated at 5 volts.
Socket 5
It operated at 3.3 volts and had 320 pins.
R Anura T6
Advanced version of the SOCKET-3. It had 235 pins and operated at 3.3 volts.
Socket 7
It is the standard for Pentium and Pentium-MMX processors. This socket also smoothly supported microprocessors from other manufacturers such as AMD K5, K6, K6-2, K6-III and Cyrix processors. It had 321 pins and operated at 2.5 to 3.3 volts.
Z local 8
It is the socket used exclusively by Pentium Pro microprocessors. It had 387 pins and operated at voltages of 3.1 and 3.3 volts.
Slot 1
It is not a ZIF type socket but an SEC type (Single Edge Connector, Simple Edge Connector). Intel patented it for its Pentium II and Celeron microprocessors. It consisted of 242 contacts and was allowed to operate in a range of voltages that oscillated between 2.8 and 3.3 volts.
Slot 2
Improved version of Slot-1 for Pentium II/III Xeon. Unlike the Slot-1, it had two notches. It had 330 pins and was allowed to operate with voltages between 1.3 and 3.3 volts.
Socket 370
It is primarily used with the latest versions of Intel’s Pentium III and Celeron microprocessors. It supports a range of voltages between 1.3 and 2.1 volts.
Slot A
A version very similar to Slot-1, although incompatible, was developed by the manufacturer AMD for its first Athlon microprocessors. It consisted of 242 contacts and allowed a range of voltages between 1.3 and 2.05 volts.
Socket A
It’s AMD’s answer to Intel’s Socket-370. The socket is used with current versions of AMD’s Athlon and Duron microprocessors.
Socket 423
On the other hand, this was specially designed to house Intel’s early Pentium 4 microprocessors. It is also called PGA423.
Socket 478
The new version of the ZIF type socket emerged as an evolution of Socket 423, but in this case with 478 pins, specially designed to accommodate the latest Intel Pentium 4 models with a 0.13 micron Northwood core. It is also called PGA478.
Socket 754 y Socket 940
In addition, they are the most recent versions of the ZIF-type socket designed to house the different 64-bit AMD microprocessors. Specifically, Socket 754 is designed for the AMD Opteron and Socket 940 for the Athlon 64.